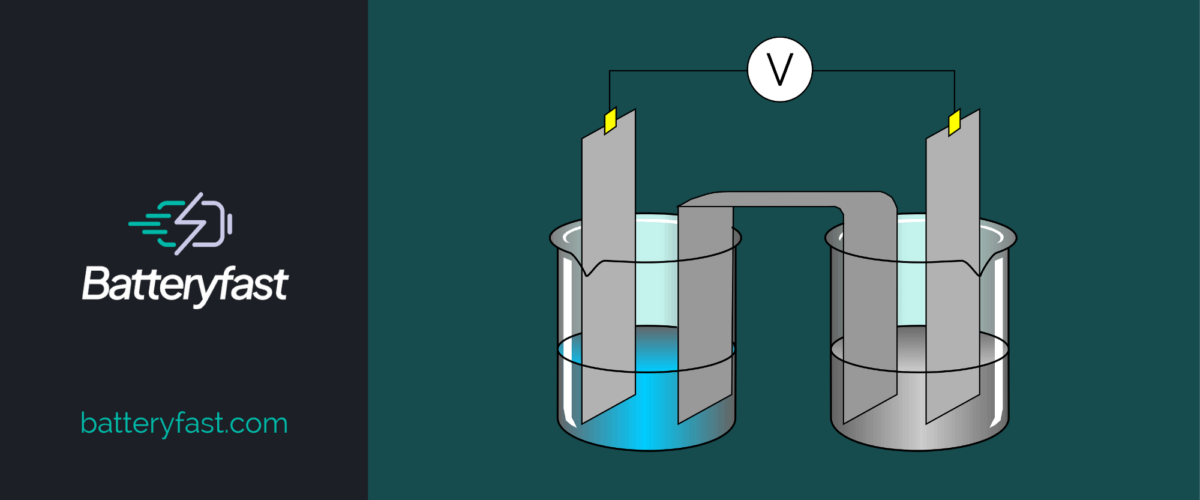
Intro
Anode and cathode are two electrode types used in electric circuits, and in processes such as electrolysis. An anode is where electrical current enters, and a cathode is where it exits. Current flow rate, or amperage, depends on voltage and resistance across a circuit.
An anode attracts positively charged particles and repels negative. A cathode does the opposite. Although, some devices can be built using one type. For example, batteries powered by their own ‘alien charge’ with just one electrode.
Anodes are usually made from metals like copper or aluminum, as they conduct electricity well. Cathodes can be metallic (zinc) or non-metallic (carbon). In special cases, electrodes need to be inert so they don’t react with solution ions or other species.
Definition of Anode and Cathode
Anode and cathode are terms used in electric circuits. Anode is positive and cathode is negative. Electrons enter at the cathode, then flow out of the anode. Voltage applied across a circuit causes electrons to move in one direction only. The polarities of voltage are labeled plus (+) or minus (-).
Anodes let electrons in easily, and resist them leaving. Cathodes have high electric potentials, emitting electrons out. Current flows from low potential cations through wires, exiting from high potential anions.
Working Principle of Anode and Cathode
Anode and cathode are two electrodes in an electrical circuit. Anode is positively charged and cathode is negatively charged. This concept can be applied to all types of electrical systems. An anode functions as a source for electrons, while a cathode acts as a sink or receiver. The direction of the electron flow depends on the type of current powering them. Care must be taken to ensure electricity flows only one way.
When electricity passes through an electrolyte solution, it splits into cations and anions. In galvanic cells, cations move towards the cathode. This causes electrons to accumulate there, making the cathode side positive. On the other hand, anions with a negative charge accumulate at anodes. This causes electrons to flow from them to balance the charge. Anodes give up electrons, cathodes absorb them.
Types of Anode and Cathode
Anodes and cathodes are key components in batteries and electroplating. They control the direction of electron current flow in a circuit. There are different types: anodes can be metal, oxide, or polymer. Examples include zinc, tin-oxide, or lead-oxide anodes.
Cathodes can be carbon or graphite, and they drive up positive charge build up. Additionally, they cast off ions from salts during discharge processes, making electrical production more efficient.
Applications of Anodes and Cathodes
Anodes and cathodes are essential components of electrical systems. They are used in many applications, like powering everyday items or industrial machines. An anode is the positively charged electrode, while a cathode is the negatively charged one. By connecting them to different power sources, electric current can be generated and controlled in a circuit.
Anodes are often used in batteries. When current flows in, it starts an oxidation-reduction reaction. This links the anode material and the battery’s electrolyte, releasing electrons. These then move to the cathode to complete the circuit and power the device.
Cathodes are also used as electrodes to create or keep currents at certain levels. Cathodic protection systems use them to protect metals from corrosion. They do this by releasing electrons into the environment around them. Cathodic processes are also used for electroplating, such as chrome-plating car bumpers or coating industrial parts with zinc. Cathodic processes also protect pipelines from corrosion. This can be done by connecting them to sacrificial anodes or using embedded circuits that monitor their environment.
Conclusion
Anode and cathode are two terminals of a voltage source. The anode is the positive terminal, releasing energy. The cathode is the negative terminal, where energy is absorbed.
Their position in the circuit or device determines their purpose. Anodes emit electrons, while cathodes absorb them. Both can do both functions in some cases.
The materials and construction for a device/circuit can be improved with different types. For example, lithium-ion batteries last longer with lithium salts at both ends. Different materials (e.g., stainless steel vs graphite) at each end also reduce degradation over time. This is due to their unique chemical composition and electrochemical processes inside the device.
Frequently Asked Questions
Q1: What is the difference between anode and cathode in a battery?
A1: The anode is the negative terminal of a battery and the cathode is the positive terminal. The anode is the source of electrons, while the cathode is the destination of electrons. The anode is where oxidation takes place, and the cathode is where reduction takes place.
Q2: What happens when an anode and cathode are connected in a battery?
A2: When an anode and cathode are connected in a battery, the anode loses electrons and the cathode gains electrons, creating an electric current. This electric current can be used to power different electrical devices.
Q3: How does the anode and cathode affect battery life?
A3: Anode and cathode have a significant impact on battery life. A battery with a more efficient anode and cathode combination can last longer. By ensuring that the anode and cathode are both in good condition, you can help extend the life of the battery.