Lithium Iron Phosphate (LiFePO4) Battery
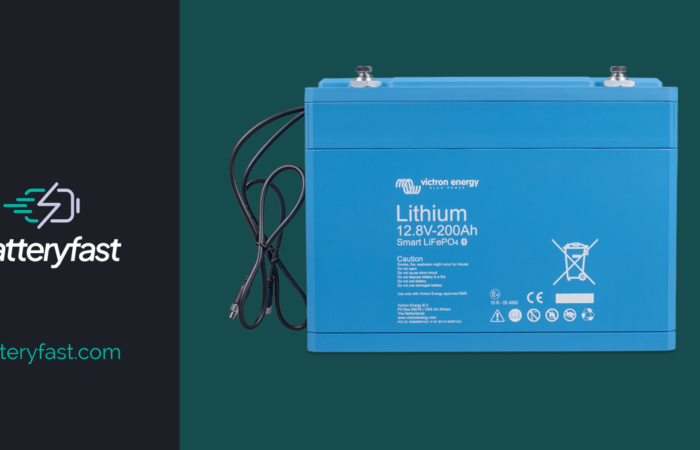
A Lithium Iron Phosphate (LiFePO4) battery, also known as LFP battery, is a type of rechargeable lithium-ion battery that uses Lithium Iron Phosphate as the cathode. It’s a relatively new technology, and has gained recent popularity due to its energy density, cycle life, and safety. Compared to other lithium-ion batteries, LiFePO4 batteries have lower energy […]